How To Run Docker Without sudo as a Non-root User in Linux
Overview:
This guide demonstrates how to configure Docker so as to run it without the sudo command as a non-root user in Linux. This is one of the key Linux post-installation steps for the Docker engine.
Page Contents
What you need to know
After installing Docker on your Linux system and running it, the Docker daemon will bind to a Unix socket which is owned by the root user. Normal users with administrative rights to the system can only run the docker command by prefacing it with the sudo command. If you don’t want to use the sudo command to run the docker command, create a system group called docker and add users to it as shown below.
Add User to Docker Group
To run the docker command without sudo, add the user to the docker group as follows. First, create the docker group. In Debian and Ubuntu as well as other mainstream Linux distributions, the docker group is created by default during the Docker package installation process:
$sudo groupadd docker
If the docker group already exists on the system, you will see the following error. Simply ignore it and proceed to the next step of adding your user to the docker group.
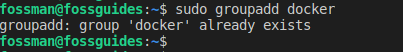
Next, add your user to the docker group. The following command will add the current user who is logged on, to the docker group:
$sudo usermod -aG docker $USER OR $ sudo gpasswd -a $USER docker
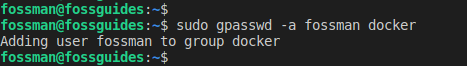
To add another user to the docker group, provide the username as shown, for example, username fossman:
$sudo usermod -aG docker fossman OR $ sudo gpasswd -a fossman docker
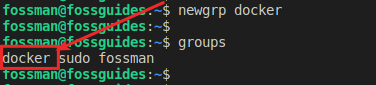
Next, log out and log in again so that that system updates your groups or run the command below:
$newgrp docker $groups
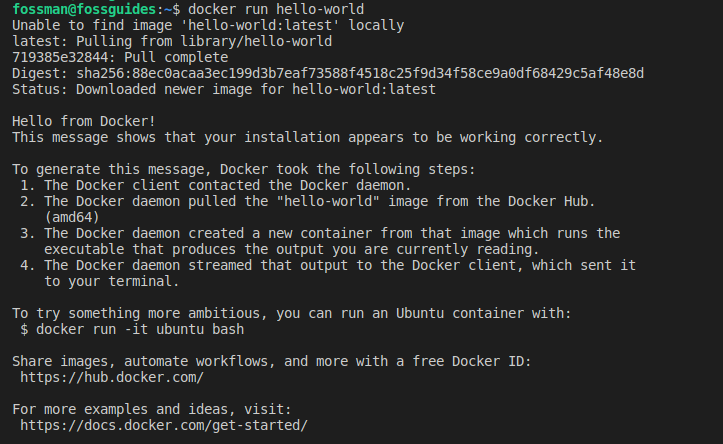
Lastly, test if you can now run the docker command without the sudo command like this:
$ docker run hello-world
Conclusion
That’s all I had for you in this guide where I showed you how to configure Docker so as to run it without the sudo command. You can ask questions or share comments via the feedback form below.